📆 Project Period | March, 2022 |
📍 GitHub |
SatExtractor
Build, deploy and extract satellite public constellations with one command line.
About The Project
TLDR: SatExtractor gets all revisits in a date range from a given geojson region from any public satellite constellation and store it in a cloud friendly format.
The large amount of image data makes it difficult to create datasets to train models quickly and reliably. Existing methods for extracting satellite images take a long time to process and have user quotas that restrict access. Therefore, we created an open source extraction tool SatExtractor to perform worldwide datasets extractions using serverless providers such as Google Cloud Platform or AWS and based on a common existing standard: STAC. The tool scales horizontally as needed, extracting revisits and storing them in zarr format to be easily used by deep learning models. It is fully configurable using Hydra.
Getting Started
SatExtractor needs a cloud provider to work. Before you start using it, you'll need to create and configure a cloud provider account. We provide the implementation to work with Google Cloud, but SatExtractor is implemented to be easily extensible to other providers.
Structure
The package is structured in a modular and configurable approach. It is basically a pipeline containing 6 important steps (separated in modules).
Builder: contains the logic to build the container that will run the extraction.
Stac: converts a public constellation to the STAC standard.
Tiler: Creates tiles of the given region to perform the extraction.
Scheduler: Decides how those tiles are going to be scheduled creating extractions tasks.
Preparer: Prepare the files in the cloud storage.
Deployer: Deploy the extraction tasks created by the scheduler to perform the extraction.
All the steps are optional and the user decides which to run the main config file.
Prerequisites
In order to run SatExtractor we recommend to have a virtual env and a cloud provider user should already been created.
Clone the repo:
git clone https://github.com/FrontierDevelopmentLab/sat-extractorInstall python packages
pip install .Usage
🔴🔴🔴
WARNING!!!!:Running SatExtractor will use your billable cloud provider services.We strongly recommend testing it with a small region to get acquainted with the process and have a first sense of your cloud provider costs for the datasets you want to generate. Be sure you are running all your cloud provider services in the same region to avoid extra costs.
🔴🔴🔴
Once a cloud provider user is set and the package is installed you'll need to grab the GeoJSON region you want (you can get it from the super-cool tool geojson.io) and change the config files.
- Choose a region name (eg
cordobabelow) and create an output directory for it:
mkdir output/cordoba- Save the region GeoJSON as
aoi.geojsonand store it in the folder you just created. - Open the
config.yamland you'll see something like this:
The important here is to set the dataset_name to <your_region_name>, define the start_date and end_date for your revisits, your constellations and the tasks to be run (you would want to run the build only one time and the comment it out.)
Important: the token.json contains the needed credentials to access you cloud provider. In this example case it contains the gcp credentials. You can see instructions for getting it below in the Authentication instructions.
- Open the
cloud/<provider>.yamland add there your account info as in the default provided file. (optional): you can choose different configurations by changing modules configs:builder,stac,tiler,scheduler,preparer, etc. There you can change things like patch_size, chunk_size. - Run
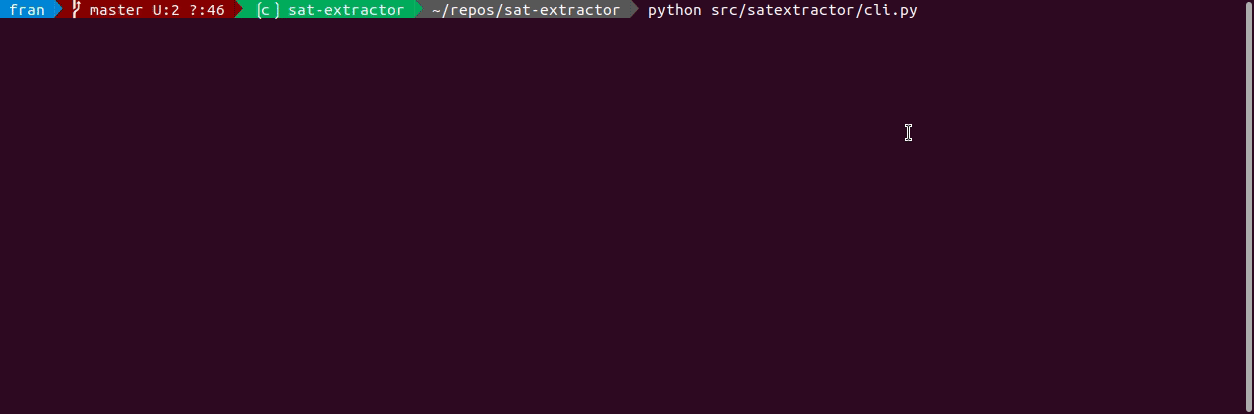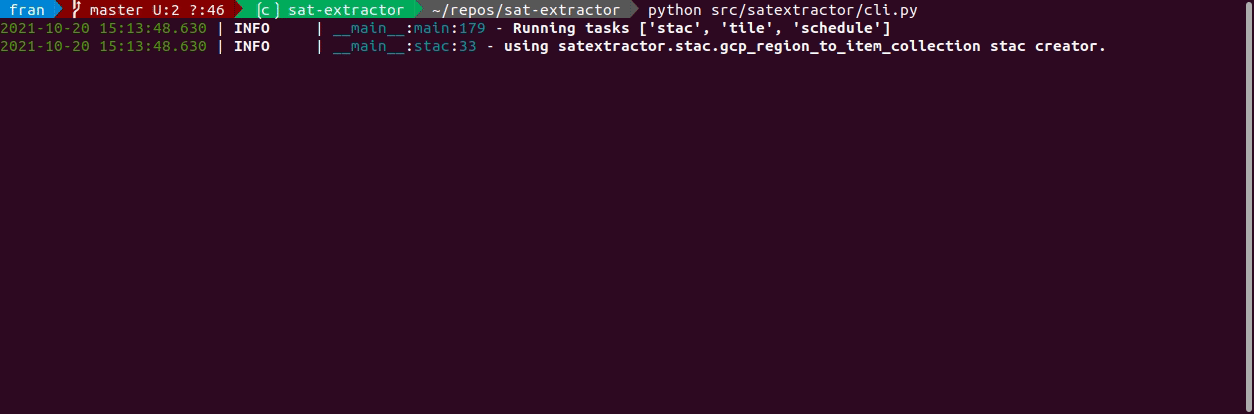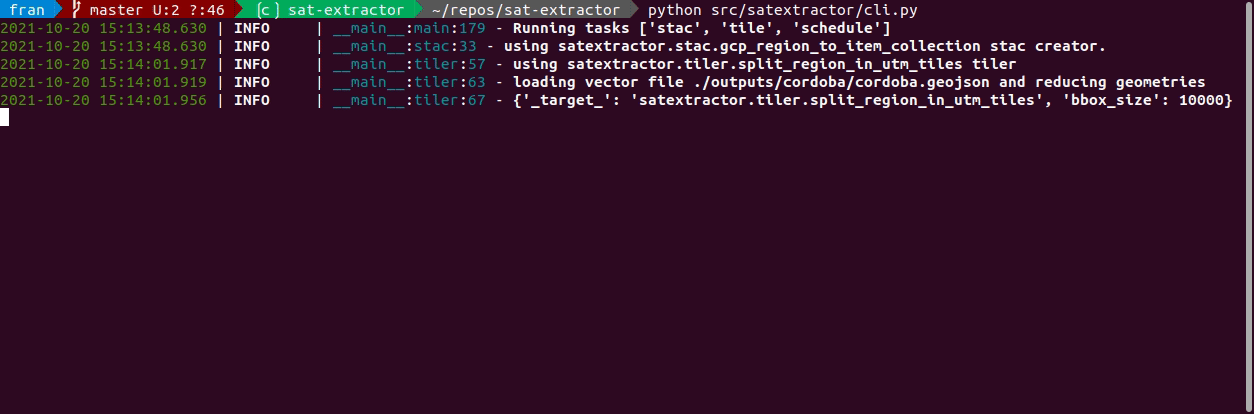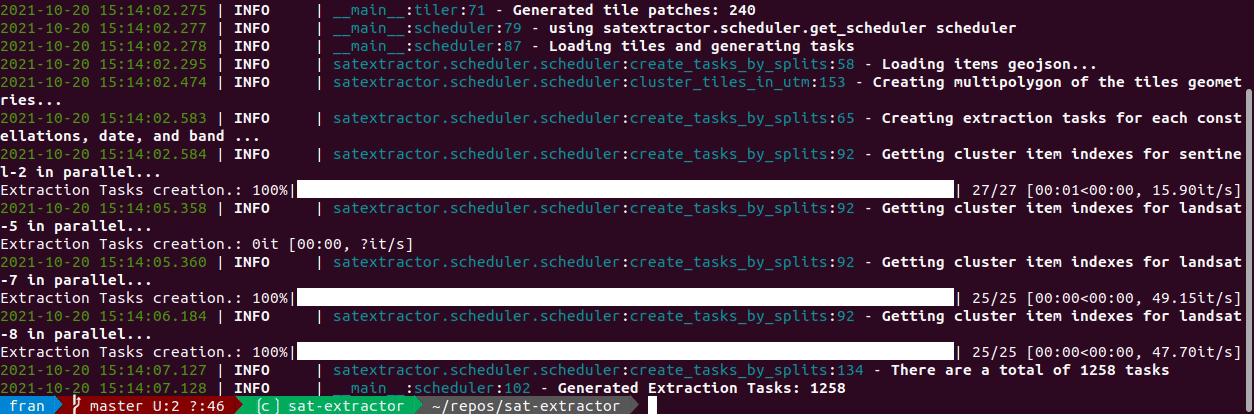
python src/satextractor/cli.pyand enjoy!
See the open issues for a full list of proposed features (and known issues).
Authentication
Google Cloud
To get the token.json for Google Cloud, the recommended approach is to create a service account:
- Go to Credentials
- Click
Create Credentialsand chooseService account - Enter a name (e.g.
sat-extractor) and clickDone(you may also want to modify permissions and users) - Choose the account from the list and then to to the
Keystab - Click
Add key->Create new key->JSONand save the file that gets downloaded - Rename to
token.jsonand you're done!
For building the sat-extractor service, you may also need to configure the credentials used by the cloud provider commandline devkit. Permissions at the project-owner level are recommended. If using Google Cloud Platform, you can authorize the gcloud devkit to access Google Cloud Platform using your Google credentials by running the command gcloud auth login. You may also need to run gcloud config set project your-proj-name for sat-extractor to work properly.
Contributing
Contributions are what make the open source community such an amazing place to learn, inspire, and create. Any contributions you make are greatly appreciated. If you have a suggestion that would make this better, please fork the repo and create a pull request. You can also simply open an issue with the tag "enhancement". Don't forget to give the project a star! Thanks again!
- Fork the Project
- Create your Feature Branch (
git checkout -b feature/AmazingFeature) - Commit your Changes (
git commit -m 'Add some AmazingFeature') - Push to the Branch (
git push origin feature/AmazingFeature) - Open a Pull Request
License
Distributed under the BSD 2 License. See LICENSE.txt for more information.
Citations
If you want to use this repo please cite:
Acknowledgments

This work is the result of the 2021 ESA Frontier Development Lab World Food Embeddings team. We are grateful to all organisers, mentors and sponsors for providing us this opportunity. We thank Google Cloud for providing computing and storage resources to complete this work.
